Biology
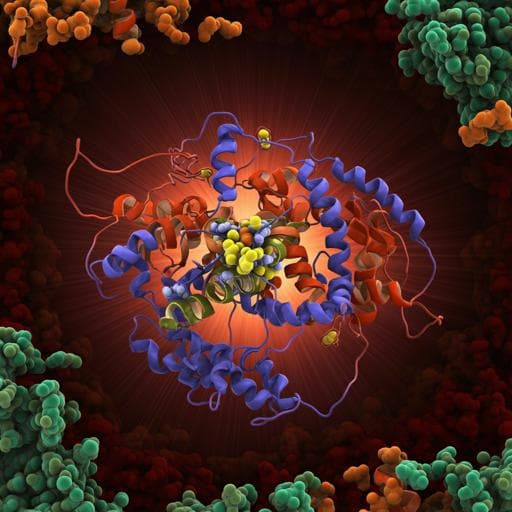
Key role of quinone in the mechanism of respiratory complex I
J. Gutiérrez-fernández, K. Kaszuba, et al.
Discover groundbreaking insights into respiratory complex I in this fascinating study by Javier Gutiérrez-Fernández and colleagues. The research reveals how quinone binding, rather than NADH, triggers significant structural changes that are crucial for understanding the energy coupling mechanism in this vital complex.
Related Publications
Explore these studies to deepen your understanding of the subject.