Chemistry
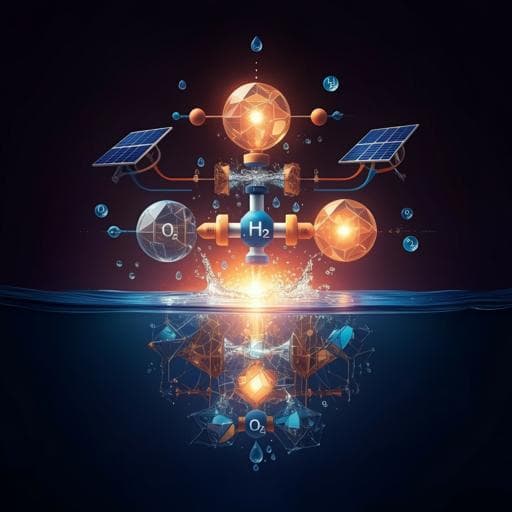
Integrated halide perovskite photoelectrochemical cells with solar-driven water-splitting efficiency of 20.8%
A. M. K. Fehr, A. Agrawal, et al.
Discover the groundbreaking work by Austin M. K. Fehr and colleagues on the innovative conductive adhesive-barrier (CAB) that enhances solar-to-hydrogen efficiencies of perovskite-based cells. Their co-planar design hit an impressive 13.4% efficiency, while a stacked tandem achieved 20.8%, revolutionizing sustainable water-splitting technology.
Related Publications
Explore these studies to deepen your understanding of the subject.