Medicine and Health
High-contrast, fast chemical imaging by coherent Raman scattering using a self-synchronized two-colour fibre laser
C. Kong, C. Pilger, et al.
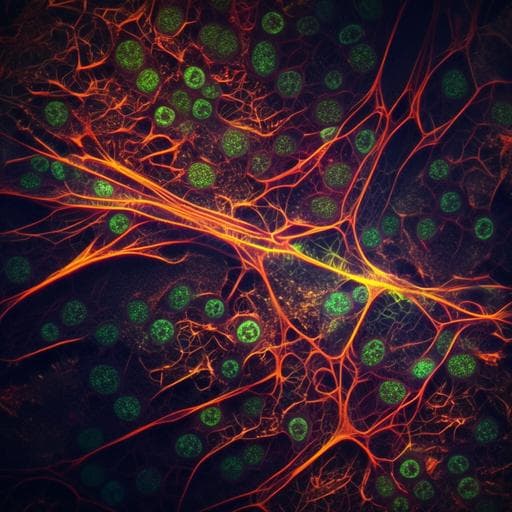
This groundbreaking research by Cihang Kong and colleagues introduces a high-power self-synchronized two-colour pulsed fibre laser that enhances the capabilities of coherent Raman scattering microscopy. The improvements in imaging quality and stability allow for high-contrast imaging of living cells and tissues, expanding the possibilities for biomedical applications.
Related Publications
Explore these studies to deepen your understanding of the subject.