Biology
Dopamine control of social novelty preference is constrained by an interpeduncular-tegmentum circuit
S. Molas, T. G. Freels, et al.
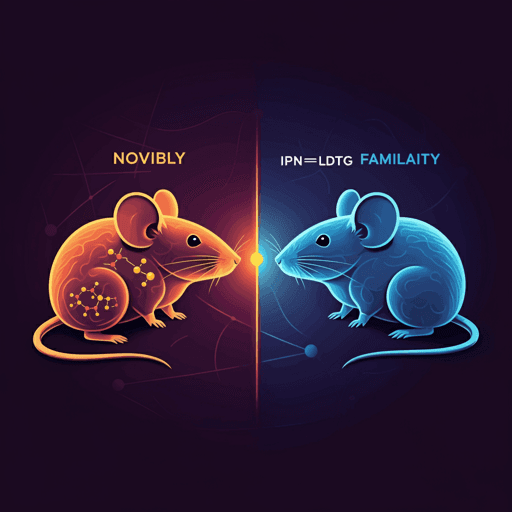
Mice preferentially explore novel over familiar social cues through strong mesolimbic dopamine responses that control interaction bout length, while an IPN→LDTg GABAergic circuit suppresses dopamine to limit familiarity-driven interactions. Using calcium and neurotransmitter sensors with fiber photometry and optogenetics, the study maps how novelty interest is encoded and regulated. This research was conducted by Authors present in <Authors> tag.
~3 min • Beginner • English
Related Publications
Explore these studies to deepen your understanding of the subject.